http://fionaw95.blogspot.com/2012/04/trust-me-trust-me-im-geographer.html
So For my geography project I have chosen animals as my interest as they are really close to my heart and I think it would be really interesting to see how they have adapted to all the different weather climates and environment challenges around them. So thats all the talk im going to be doing so sit back and enjoy my project :)
oh and P.s feel free to ask any questions or point out if I have made an error with my information :)
To start things off here is a map of the worlds and its continents. I have Chosen to take one animal from each continent and study how it has adapted to the different climate and habitat in the chosen continent.
Continents:
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Asia
- Africa
- Australia
- Antarctic
First Stop on our Trip is North America
The Animal I Have chosen to study in North America is (drum role please) The Elk.

Elk are also called wapiti, a Native American word that
means "light-colored deer". Elk are related to deer but are much
larger than most of their relatives. A male Elk is called a Bull while a female
Elk is called a Cow.A bull elk's antlers may reach 4 feet above its head, so
that the animal towers 9 feet tall! They have cloven hooves with fairly pointed
toes, so they leave two-pronged tracks on the ground.Elk colouration varies
from a copper-like tone to more of a beige, with a lighter-coloured patch of
hair on the rump. Many times, their neck and legs will be darker than the rest
of their body.The colour of their coats makes great camouflage in the forest
area, protecting them from predators and hunters. Groups of Elk are called a Gang. Here is a picture of Elk to human height ratio;


Living in mainly
mountain meadows and forests The Elk has adapted to its habitat by being
a herbivore and living on a diet of grass, plants, bushes and saplings. But an
interesting fact about elk is that they are so adaptable that in some
non-native areas where they've been introduced, they have come to threaten
native animal populations, which have a hard time competing with the elk's need
to eat as much as fifteen pounds of vegetation per day. Elk usually herd in
groups, so there are always a pair of eyes ready to spot potential danger. The
position of their eyes make them capable to see danger approaching from almost
any direction. As with other deer, the elk's mating season is called the rut.
It occurs in the fall of the year, and may peak any time from the second week
of September through about the same part of October. After breeding, the
gestation period is about 250 days, so births occur roughly eight months after
the act. This allows the young to enjoy the milder weather of spring, rather
than having to fight through winter, which can be brutal in some areas of the
elk's range.
Elk communicate in a wide variety of ways, using calls, scents,
and visual cues. Calls include barks, mews, squeals, grunts, coughs, and the
bugle, which is probably the best-known of all elk vocalizations.Visual cues
are often seen in the way a bull walks, runs, or generally presents himself to
other elk. This may mean a challenge, submission, or simply, hello. Here is a video of an Elk's Bugle:
Next stop on our trip is to... South America
The Animal I Have chosen to study in South America is (drum role please) The Amazonian Manatee!





Next stop on our trip is to... South America
The Animal I Have chosen to study in South America is (drum role please) The Amazonian Manatee!


The Amazonian Manatee or Trichechus inunguis is a species of manatee that lives in the fresh water habitats of the Amazon River.They live exclusively in freshwater and prefer blackwater lakes, oxbows and lagoons. They are mainly solitary but sometimes they will gather in small groups consisting of up to 8 individuals.
The amazonian manatee is also known as a seacow. It is dark grey with white or pink or patches on it belly. they have a sparse scattering of short hair on their body. Their skin is thick and beneath it they have a layer of fat. The amazonian manatee is the smallest of manatee species apart from the dwarf manatee and usually has no main predation apart from occasionally being hunted by humans. Manatee have a life expectation of up to 60 years. It may reach a length of 3m. Females are typically larger than males and can weigh 360 to 540 kg. Unlike the West Indian manatee, it lacks nails on the end of most flippers allowing it to agile easily through the water. They have a small head with a broad muzzle that is adapted for feeding on aquatic plants. Their eyes are small and they rely on their senses of hearing and touch.
Amazonian Manatees feed on abrasive plants and because of this their teeth are constantly being worn down. To counteract this their teeth are continually being replaced throughout their life.They mainly feed during the wet season when new vegetation is abundant, but they may fast for weeks or months during the dry season when food is scarce.
Amazonian Manatees tend to breed throughout the year, although in some areas of the Amazon Basin breeding is seasonal. After a gestation period of 12 months a single calf is born. After a few weeks the calf will begin to eat vegetation but they will stay with their mother for 12 - 18 months until they are weaned. When females begin to reproduce they will give birth every second year.
A picture of human to manatee height ratio; A picture of where they can be found;


Next stop on our trip is to... Australia
The Animal I Have chosen to study in Australia is (drum role please) The Duck Billed Platypus!



They have short, thick fur which is colored dark brown on their back, but lighter on their underside. They have short limbs with webbed front feet and partially webbed hind feet. Males are also venomous. They have sharp stingers on the heels of their rear feet and can use them to deliver a strong toxic blow .Their bill is flexible and their tail is broad and flat and is used to aid swimming and to store fat reserves, an adaptation it shares with the Tasmanian devil. They rest in their burrows during the day and they are mainly active at night. They are excellent swimmers and they spend most of their time in the water. They can close their nostrils, eyes and ears to prevent water from entering them when they dive below the surface.Platypuses are known to emit a low growl if they are disturbed and several other vocalizations have been herd being emitted from captive animals. A video of a Platypus growl:
The Animal I Have chosen to study in Australia is (drum role please) The Duck Billed Platypus!


Duck-Billed Platypuses are found in the lakes, streams and rivers of eastern mainland Australia and Tasmania.They build their burrows in banks, with the entrance above the surface of the water. Duck-Billed Platypuses have territories of up to 7 kms and the territory of a male will overlap with the territories of 3 - 4 females.
Duck-Billed Platypuses are semi-aquatic mammals. They have a body length between 40 and 60 cms, a tail length between 8.5 and 15 cms, a bill of 5cms and weigh between 1-2.5kgs. Males are larger than females and there are size variations depending on their location and the season. Picture or Human to Platypus height ratio:

They have short, thick fur which is colored dark brown on their back, but lighter on their underside. They have short limbs with webbed front feet and partially webbed hind feet. Males are also venomous. They have sharp stingers on the heels of their rear feet and can use them to deliver a strong toxic blow .Their bill is flexible and their tail is broad and flat and is used to aid swimming and to store fat reserves, an adaptation it shares with the Tasmanian devil. They rest in their burrows during the day and they are mainly active at night. They are excellent swimmers and they spend most of their time in the water. They can close their nostrils, eyes and ears to prevent water from entering them when they dive below the surface.Platypuses are known to emit a low growl if they are disturbed and several other vocalizations have been herd being emitted from captive animals. A video of a Platypus growl:
Platypuses hunt underwater, where they swim gracefully by paddling with their front webbed feet and steering with their hind feet and beaver-like tail. The diet of a Duck-Billed Platypus mainly consists of invertebrates that live on the bottom of lakes, rivers or streams. Occasionally they will also eat fish, insects or frogs. They use their bill to navigate through murky water to locate their food. Platypuses do not have teeth, so the bits of gravel help them to chew their meal.The main predators of Duck-Billed Platypuses are snakes, water rats, monitor lizards, hawks, owls and eagles.
Duck-Billed Platypuses breed between July and October. Mating occurs under water and after a gestation period of approximately 2 - 3 weeks 2, occasionally 3, soft shelled eggs are laid. The female curls herself around her eggs and incubates them for approximately 10 days.
When the young hatch they are blind and hairless and they feed only from their mother's milk. Females lack teats and instead milk is secreted from pores in the skin. The young are able to lap up her milk from the pools that collect in the grooves of her abdomen.
The young Platypuses emerge from the burrow when they reach approximately 4 months old. Females are thought to become sexually mature in their second year.
Picture of a baby platypus:

Next stop on our trip is to... Africa!
The Animal I Have chosen to study in Africa is (drum role please) The African Wild Dog.




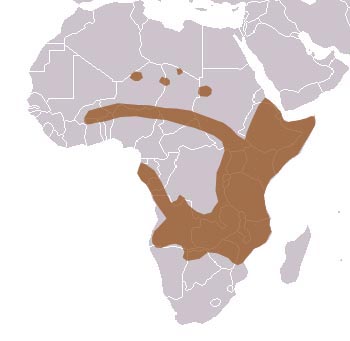



The Animal I Have chosen to study in Africa is (drum role please) The African Wild Dog.


The African wild dog, also called Cape hunting dog or painted dog, typically roams the open plains and sparse woodlands of sub-Saharan Africa. African wild dogs usually live in packs of up to 15 adults together with their young. Each pack has two dominant adults, one male and one female. Usually only the dominant pair will mate, but all members of the pack will look after the young.After a gestation period of 69 - 72 days, 2 - 16 pups will be born in a den. When they are born they are helpless, colored black and white, and their eyes and ears are closed.For the first month they will feed on milk but after this the pups will eat regurgitated food. At 3 months old the pups are weaned and at 6 months old they will join the pack to hunt. Picture of African Wild Dog Pups:
Their coats are colored, black, tan and white and they each have unique, irregular markings. Their hair is fairly sparse and their skin is black in color. They have long, slender limbs and they are unique canids, in that they only have four toes. Their head is large, with big, rounded ears and a short, powerful muzzle.When hunting they can reach speeds up to 45 km/hr and they communicate using chirping or squeaking sounds. Video of African Wild Dog chirping:
African Wild Dogs are exclusively carnivorous and they mainly feed on gazelle, zebra, impala, wildebeest, hares, rodents and other small animals. The pups are the first ones to feed at a kill and members of the pack will regurgitate food to feed those that stayed at the den.
African Wild Dogs have no natural predators however their main threats are disease and habitat fragmentation.
Picture of human to African wild dog height ratio: Map of where they can be found:


Next stop on our trip is to... Asia!
The Animal I Have chosen to study in Asia is (drum role please) The Snow Leopard.


Snow Leopards are found in Central, South and East Asia. They inhabit areas of mountain steppes and forest scrub at altitudes of 2000 - 6000 metres. The climate in these areas is harsh, cold and dry.They are solitary animals, except mothers with cubs, and males and females have been known to hunt together during the breeding season
A Snow Leopards diet is mainly made up of wild sheep and goats but it also consists of yak, asses, pikas, marmots, hares, musk deer, birds and domestic livestock.They are opportunistic predators and they mainly stalk or ambush their prey.Their primary predator is man, but they are also preyed upon by wolves.
Snow Leopards are exceptional athletes and they can bring down prey almost three times their own size.They are insulated by thick hair, and their wide, fur-covered feet act as natural snowshoes.Their fur is very thick and it is grey in color with brown/black markings. Their markings consist of spots around their neck and lower limbs and rosettes on other parts of their body. These markings help to camouflage them on the rocky slopes so they can sneak up on their prey. Snow leopards have powerful legs and are tremendous leapers, able to jump as far as 50 feet.They use their long tails for balance and as blankets to cover sensitive body parts against the severe mountain chill.
A picture of human to Snow leopard height ratio:

After a gestation period of 98 - 104 days 1 - 5 cubs , commonly 2 - 3, are born in a den. They are born helpless and with their eyes closed , opening their eyes within 7 days. At 2 months old the cubs are eating solid food and at 3 months old they begin to follow their mother around.
The cubs stay in the company of their mother until they are between 1 and 2 years of age after which they leave to find their own territory.Females become sexually mature at 2 - 3 years of age while males reach sexual maturity at approximately 4 years of age. Snow Leopards mate between January and March and after mating the pair go their separate ways, with the female preferring to do all of the parenting herself. Due to the length of time the cubs stay with their mother, Snow Leopards mate every other year.



No comments:
Post a Comment